Centre for Language and Brain Conducts First Neurolinguistic Field Study of Reading in Yakut

In July, a team from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, in collaboration with the Centre for the Study, Preservation, and Development of Native Languages of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), conducted the first-ever neurolinguistic expedition to the village of Churapcha to study reading in the Yakut language using electroencephalography (EEG). For the first time, EEG data from 43 adults and behavioural data from 40 children was collected during the two-week expedition.
According to Olga Dragoy, Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain and head of the expedition, experimental linguistics worldwide still relies primarily on data from a small number of well-studied languages, mostly from the Indo-European family. As a result, she argues, it is methodologically unsound to draw universal conclusions about the nature of language from such a limited dataset. The objective of the Centre for Language and Brain is to expand both the geographical reach and linguistic diversity of experimental linguistics. Russia, with its multilingual population, offers unique opportunities for this, being home to languages from a wide range of families and groups.
Prior to this expedition, no psychoneurolinguistic research had ever been conducted using material from the Yakut language. The first experiment of this kind was carried out in Churapcha by a team consisting of Olga Dragoy, Olga Tuzhik, and Polina Pilipets from the Centre for Language and Brain and Nadezhda Vasilyeva from the Centre for the Study, Preservation and Development of Native Languages of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
The choice of the village of Churapcha was intentional, as 99% of the local population speaks Yakut, making the Churapcha district a unique setting for studying native language perception in the context of active Yakut–Russian bilingualism.
During the two-week expedition, the team collected EEG data from 43 adults and behavioural data from 40 children. Adult participants were shown sentences containing incorrect tense coordination. The researchers recorded event-related brain potentials using EEG, enabling them to observe how the brain responds to different types of language errors.
‘The Yakut language distinguishes between an immediate past tense—eg, üleleetim, meaning "I have been working (recently)"—and a distant past tense, as in üleleebitim, meaning "I worked (a while ago)." We are interested in how the brains of native Yakut speakers respond to tense agreement errors between adverbs and verbs,' explains Polina Pilipets, Research Assistant at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
For instance, some sentences in the experiment combined the adverb bylyryyn ('a year ago,' indicating distant past) with a verb in the immediate past tense, or paired the adverb subu aghay ('just now,' indicating immediate past) with a verb in the distant past tense.

'According to preliminary surveys of native speakers, sentences that combine a distant-past adverb with a verb in the immediate past tense are perceived as more "incorrect." We expect this distinction to be reflected in the EEG signals—specifically, in the form of larger evoked potential amplitudes in response to the more prominent error,' comments Olga Tuzhik, Research Assistant at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
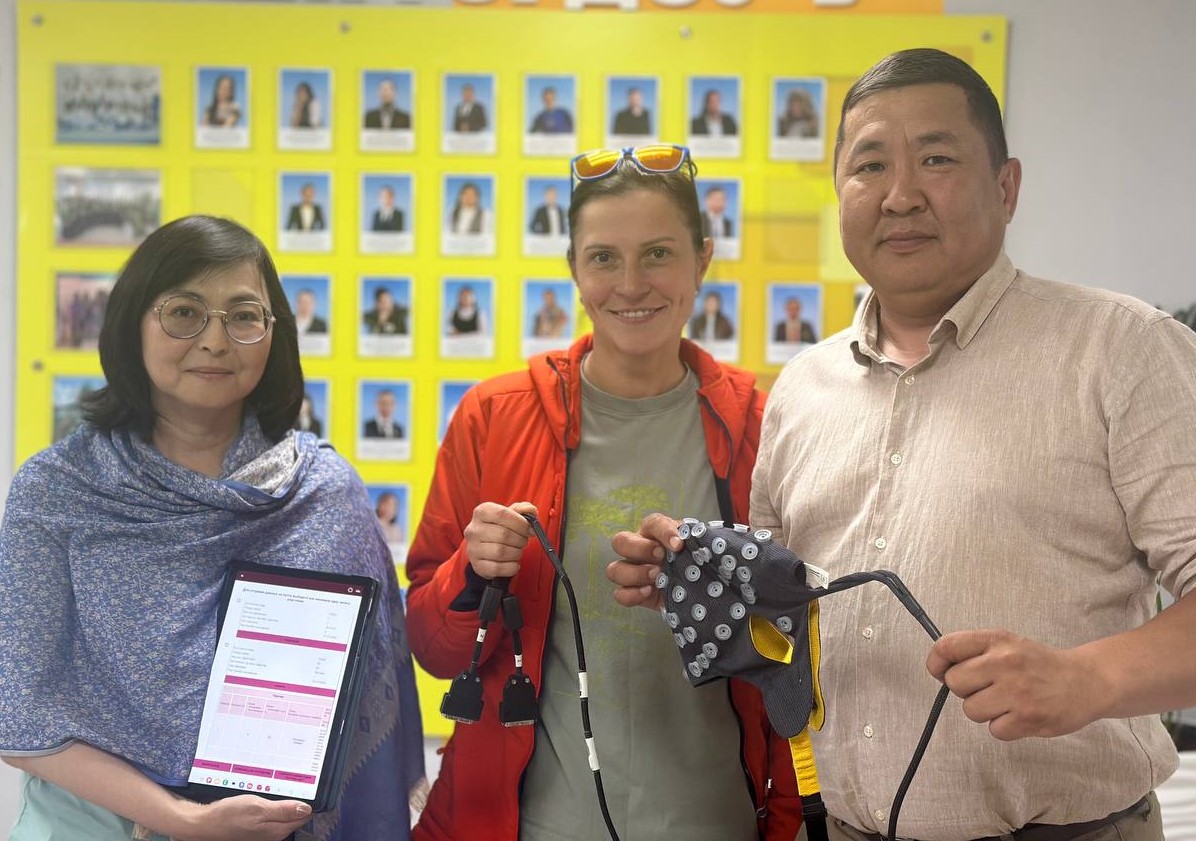
Alongside the EEG experiment, the team conducted behavioural testing with 40 bilingual children who speak both Yakut and Russian. The children completed cognitive tasks in both languages, including the RAVLT and the Trail Making Test in Russian, as well as tasks in Yakut. During the expedition, the researchers, in collaboration with linguists and native speakers, adapted the Russian-language LexiMetr test for assessing children's reading skills in Yakut and collected data in both languages.
'Adapting diagnostic tools for the Yakut language is of great importance, as it enables early diagnosis and support of children with reading difficulties. These tools are essential for both teachers and psychologists,' emphasises Nadezhda Vasilyeva, Leading Researcher at the Centre for the Study, Preservation and Development of Native Languages of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).

The expedition to Churapcha marked the first step toward a systematic study of the Yakut language using neurolinguistic methods. Moving forward, the researchers plan to examine aphasia in Russian–Yakut bilinguals. Similar studies have long been conducted in Russia with respect to the Russian language, but it remains unclear how aphasia manifests in Yakut or what specific language disorder patterns occur in native Yakut speakers. Yakutia offers all the necessary conditions for this research. In particular, the M.E. Nikolaev National Centre of Medicine is equipped with modern neurological and diagnostic facilities and has already expressed its willingness to collaborate.
'I would like to commend the excellent organisation of this expedition. It was the first time we experienced such a high level of collaboration: our colleagues from the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) and the administration of the Churapcha district ensured flawless logistics, accommodation, and participant recruitment and motivation. It was truly an inspiring experience,' Olga Dragoy concluded.
See also:
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
IDLab: Fascinating Research, Tough Deadlines, and Academic Drive
The International Laboratory of Intangible-driven Economy (IDLab) was established at the HSE campus in Perm 11 years ago. Its expertise in data processing and analysis allows researchers to combine fundamental studies with applied projects, including the development of risk and cybersecurity models for Sber. The head of the laboratory, Professor Petr Parshakov, and Senior Research Fellow Professor Mariya Molodchik spoke to the HSE News Service about IDLab’s work.
HSE Lecturers Awarded Yandex ML Prize 2025
The Yandex ML Prize is awarded to lecturers and heads of educational programmes who contribute to the development of artificial intelligence in Russia. This year, 10 laureates were selected from 300 applicants, including three members of the HSE Faculty of Computer Science (FCS). A special Hall of Fame award was also presented for contributions to the establishment of machine learning as an academic field. One of the recipients was Dmitry Vetrov, Research Professor at the HSE FCS.
HSE University and Banking and Finance Academy of Uzbekistan Sign Memorandum on Scientific Cooperation
The partnership aims to foster academic collaboration in the fields of global economics, sustainable development, and Islamic finance. Strengthening academic ties with Uzbekistan represents a promising direction for scientific exchanges and the implementation of international projects in sustainable development.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Mistakes That Explain Everything: Scientists Discuss the Future of Psycholinguistics
Today, global linguistics is undergoing a ‘multilingual revolution.’ The era of English-language dominance in the cognitive sciences is drawing to a close as researchers increasingly turn their attention to the diversity of world languages. Moreover, multilingualism is shifting from an exotic phenomenon to the norm—a change that is transforming our understanding of human cognitive abilities. The future of experimental linguistics was the focus of a recent discussion at HSE University.
‘To Help Make the World More Sustainable, Fair, and Humane’
The BRICS International School: New Generation has concluded at HSE University, bringing together more than 100 participants from 38 BRICS and Global South countries. The attendees included early-career researchers, diplomats, entrepreneurs, journalists, and civil society representatives.